

The adjusted basis is the original cost of the asset (cost-basis) adjusted for changes in the asset’s value due to depreciation (which would decrease the value of an asset) or improvements to the asset (which would increase the value of the asset). Capital Gains TaxationĪ capital gain is the difference between an estimate of the fair market value and the adjusted basis of an asset. In the final section, we offer some general conclusions. We present simulation results of the proposal analyzed in this study, and examine how inflation may affect the negative economic effects of the policy changes. We then describe how inflation will likely exacerbate the negative economic effects of these policy changes. We begin by discussing the structure of capital gains taxes. As under current law, capital gains from the sale of a primary residence would receive an exclusion of up to $250,000 ($500,000) for single (joint) filers. The Biden proposal would tax longterm capital gains at ordinary income tax rates for those with taxable income above $1 million and tax unrealized gains at the time of death (i.e., repealing step up of basis) for single (joint) filers with more than $1 million ($2 million) in unrealized gains. In this paper, we examine the economic effects of enacting the Biden Administration’s proposal to increase the taxation of long-term capital gains. Finally, two decades of relatively slow economic growth call for increased innovation and faster diffusion of new technology, but higher capital gains tax rates will reduce innovation and technology diffusion. Higher levels of inflation would exacerbate the negative economic effects of raising capital gains tax rates and repealing step up in basis. Real wages decrease initially by 0.2 percent, by 0.2 percent five years after enactment, and by 0.6 percent in the long run.
#PREFERENTIAL TREATMENT OF CAPITAL GAINS FULL#
Initially hours worked declines by 0.1 percent in a full employment economy if instead labor hours worked per individual were held constant, this would be roughly equivalent to a loss of approximately 209,000 jobs in that year. Simulations show that in the long run GDP falls by roughly 0.3 percent, as a result of a decline in the capital stock of roughly 1.0 percent and a decline in total hours worked of 0.1 percent, and aggregate consumption falls by 0.1 percent.
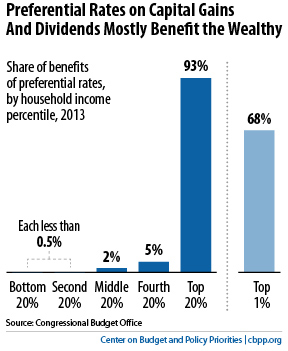
It also exacerbates the differential treatment of current and future consumption, that is it discourages saving, that occurs under an income tax. In particular, rising inflation would exacerbate the negative economic effects associated with taxing capital gains income at a higher rate as well as repealing step up in basis. Current economic conditions may exacerbate the problems associated with increasing the taxation of capital gains. In this paper, we examine the economic effects of enacting a proposal by the Biden Administration to tax long term capital gains at ordinary income tax rates for those with taxable income above $1 million and tax unrealized gains at the time of death (i.e., repealing step up of basis) for single (joint) filers with more than $1 million ($2 million) in unrealized gains.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
